ACT
American College Test
THE ACT (AMERICAN COLLEGE TEST)
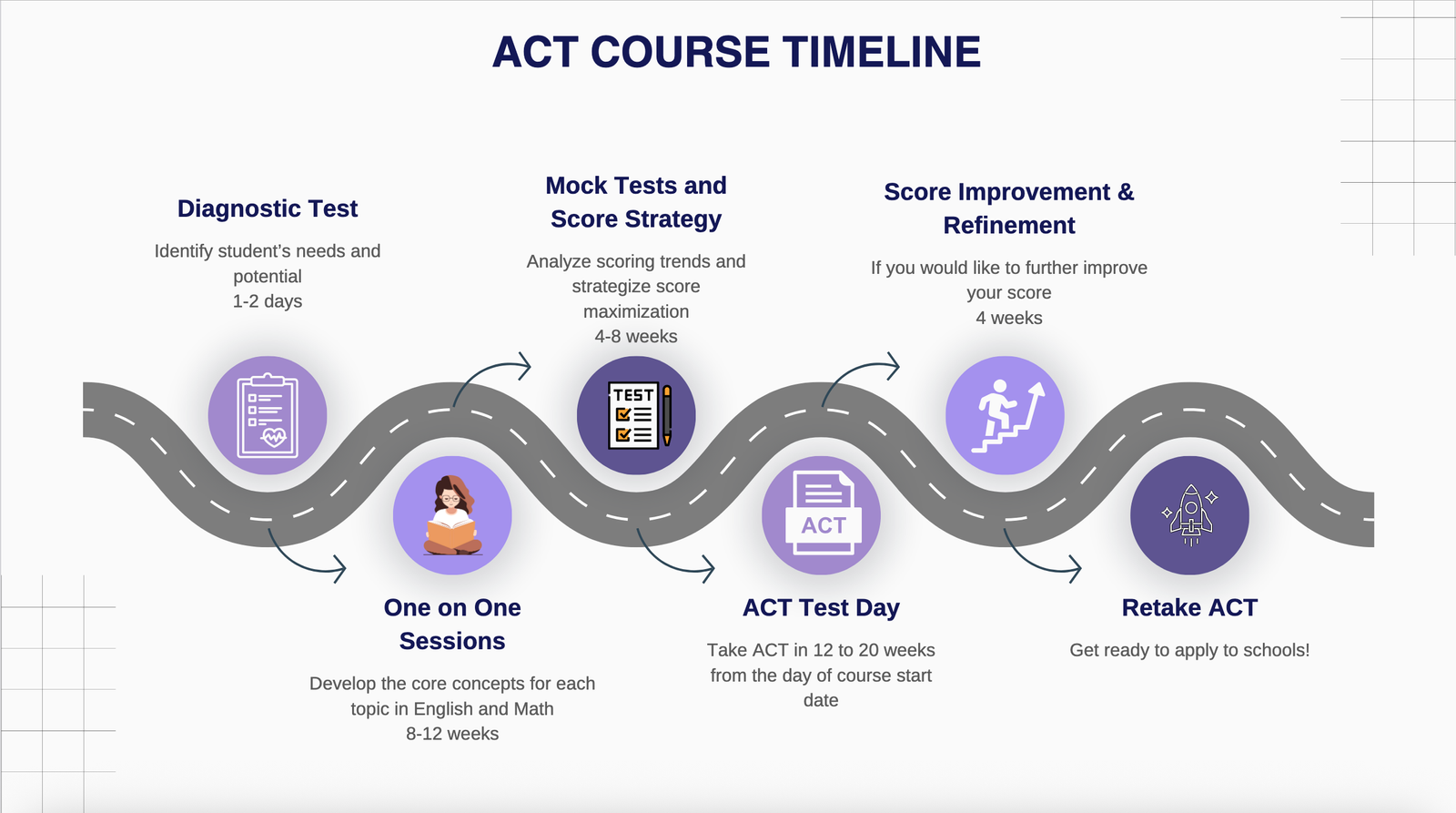
The ACT is a major college admissions test, administered by ACT, Inc. The ACT is often described as more curriculum-based than SAT – it tests knowledge and skills taught in school subjects.
CONTENT AND FORMAT
The ACT consists of four sections: English, Math, Reading, and Science, always in that order, with an optional Writing (essay) at the end. It is traditionally a paper-and-pencil test (bubble sheet), although an online version is offered at certain testing centers and the ACT is planning broader computer-based rollout by 2025. The exam’s timing is a critical factor: the ACT without writing takes 2 hours 55 minutes (175 minutes) to complete, making it slightly longer than the SAT. With the optional essay, it stretches to about 3 hours 35 minutes. Unlike the SAT’s two longer sections, the ACT’s testing time is split into four timed sections:
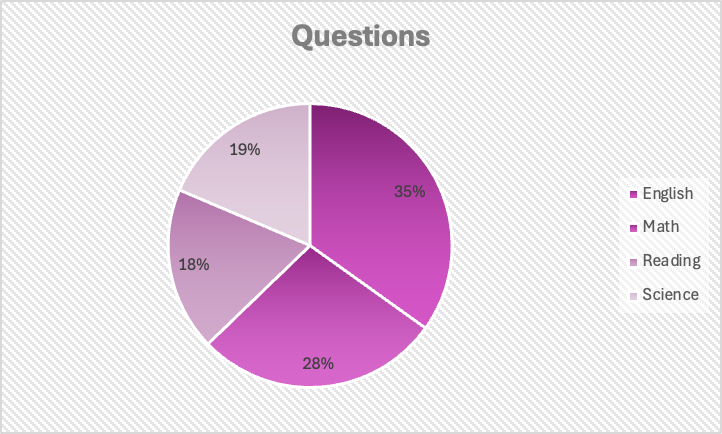
- English: 45 minutes for 75 questions.
- Math: 60 minutes for 60 questions.
- Reading: 35 minutes for 40 questions.
- Science: 35 minutes for 40 questions.
There is a short break after Math. The ACT is known for its brisk pace – students must work quickly through relatively straightforward questions. For example, in the Reading section,only 35 minutes are given for 40 questions, so time per question is about 52 seconds (passages are longer compared to SAT). The Science section, unique to the ACT, doesn’t test recall of science facts but rather interpretation of graphs, experiments, and scientific information. The optionalACT Writing test (40 minutes) presents a prompt on an issue and asks for an analytical essay; few colleges require it today, but it can showcase writing skills.

SCORING
The ACT uses a 1–36 scale for each of the four main sections (English, Math, Reading, Science). A student’s Composite scoreis the average of the four section scores, rounded to the nearest whole number. For instance, if someone scores 30 English, 28 Math, 32 Reading, 34 Science, the composite is (30+28+32+34)/4 = 31. The highest possible score is 36 (equivalent to 1600 on SAT). The optional Writing is scored separately on 2–12 and does not factor into the composite. ACT score reports also provide subscores and an optional STEM score (average of Math and Science) for students who take the Science section. As with the SAT, there is no penalty for guessing on the ACT. Many colleges will “superscore” the ACT, meaning they consider the highest section scores across multiple test dates (and ACT, Inc. now offers an official superscore calculation if you’ve taken it multiple times) as part of admissions.
PREPARATION
Prepping for the ACT involves practicing efficiency and timing. Students should familiarize themselves with the test’s fast pace, tackling 75 English questions in 45 minutes means quickly spotting grammar errors. Timed full-length practice tests are crucial to build stamina for four back-to-back sections. For ACT Math, reviewing a broad range of math topics (including geometry and some trigonometry) is key. It’s helpful to learn strategies like identifying main ideas and using the process of elimination quickly. Because the ACT permits section order and answer changes only within each section’s time, time management is critical. Students often take the ACT in between October and January of 11th Standard. As with the SAT, two attempts are common. Finally, check whether the colleges on your list superscore the ACT; if so, focusing on improving weaker sections on a second attempt can raise your composite.